Why are the Himalayas among the many most earthquake-prone areas on the planet?
The easy reply is the continued collision between the Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates. Because of this, there have been periodic earthquakes which have destroyed many lives and properties.
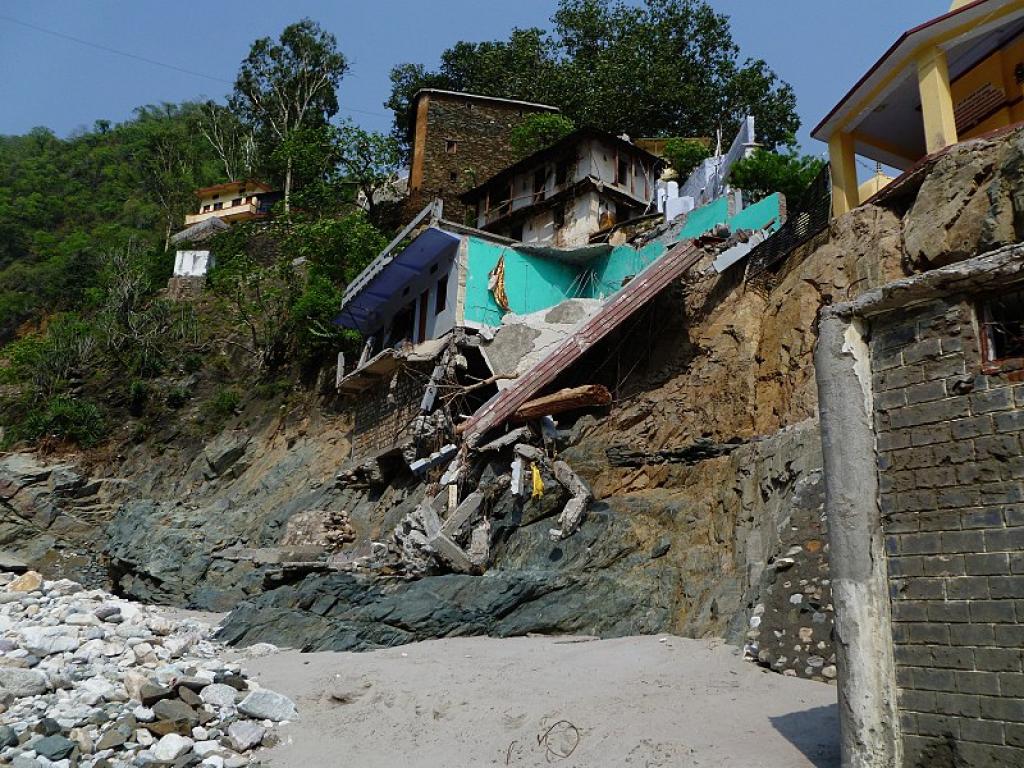
In 2005, for instance, the Kashmir area witnessed a devastating earthquake that killed over 1,350 on the Indian facet of the border, injured greater than 1,00,000, and destroyed hundreds of houses.
Responding to those important circumstances, researchers at IIT-Mandi — led by Dr Sandip Kumar Saha, assistant professor on the Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering — have developed a comparatively easy methodology to evaluate the power of bolstered concrete (RC) buildings within the Himalayan area to resist earthquakes.
In a paper co-authored by his analysis college students Yati Aggarwal and revealed within the Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering final month, they state that this methodology permits decision-makers to prioritise any strengthening and restore work that should be undertaken to boost the constructing’s resistance to earthquakes.
What is that this methodology?
Step one to make sure the earthquake security of present constructions is to evaluate their present vulnerabilities and strengths. It’s neither bodily nor economically viable to conduct an in depth seismic vulnerability evaluation of each constructing.
Speedy Visible Screening (RVS) of buildings is usually carried out to evaluate constructing vulnerabilities at a big scale. RVS makes use of visible info to resolve if a constructing is protected to occupy, or requires rapid engineering work for enhancing earthquake security.
The strategy developed relies on speedy visible screening (RVS) of buildings.
“This isn’t a wholly new method. Nevertheless, we’ve got tried to enhance the present methodology by incorporating region-specific vulnerability options. On this, the constructing is visually screened inside 15-20 minutes and totally different options which are anticipated to lower or improve the efficiency of the constructing are famous,” explains Dr Saha.
However what are these Himalayan region-specific vulnerability options?
“Whereas assessing the constructing, the assessor ought to look into the presence of irregular options, akin to enough distance between two buildings, heavy overhang, setback, irregular plan form, buildings configuration (constructing resting on flat land or slope), comfortable story, seen structural damages, framing motion, web site situations, seismic zone, variety of tales, kind of occupancy, and many others,” explains Yati Aggarwal, a PhD scholar at IIT Mandi.
“Based mostly on these noticed options, scoring of the constructing is completed. This methodology doesn’t recommend any particular restore to be carried out for strengthening a constructing. Nevertheless, it helps to segregate the buildings that require minor to vital engineering intervention which can embody a minor upkeep or a significant strengthening work,” notes Dr Saha.

How do present RVS strategies work?
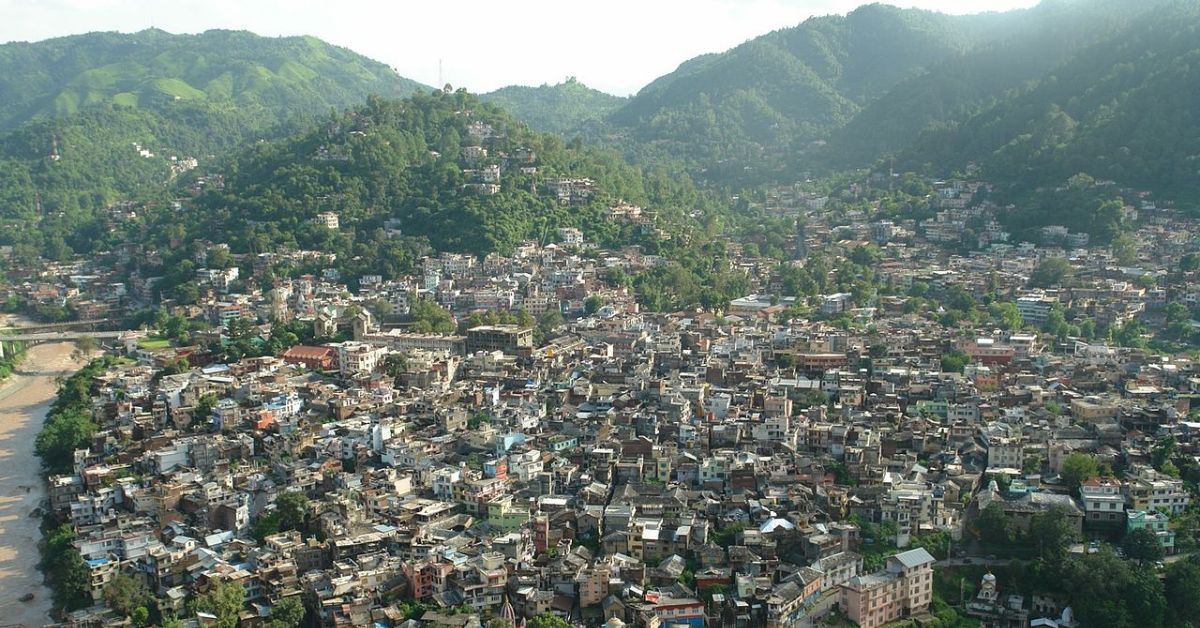
Current RVS strategies are based mostly on knowledge from totally different international locations and aren’t significantly relevant to the Indian Himalayan area, due to some traits which are distinctive to the buildings on this area.
For instance, the Himalayan area has many non-engineered constructions. There’s additionally chaotic distribution and progress of infrastructure on account of a lack of expertise amongst native building staff and poor planning by stakeholders.
“Non-engineered practices aren’t unusual for developing bolstered concrete buildings in India. If we discuss particularly about Himalayan area, a number of buildings have their basis at a number of ranges to match the bottom slope,” says Dr Saha, talking to The Higher India.
He continues, “The vulnerability options used to evaluate these buildings are derived from the intensive discipline survey in addition to from earlier post-earthquake reconnaissance experiences. The foremost distinction, whereas assessing the bolstered concrete buildings for its vulnerability, lies within the norm used for counting the variety of tales and the constructing configuration having basis at a number of ranges.”
It’s due to this fact important to make use of a region-specific RVS guideline that considers components like native building practices, typology, and many others.
“We now have devised an efficient methodology to display RC buildings within the Indian Himalayan area in order that restore work could also be prioritised in keeping with the situation of the buildings and the danger from impending earthquakes will be minimised,” he provides.
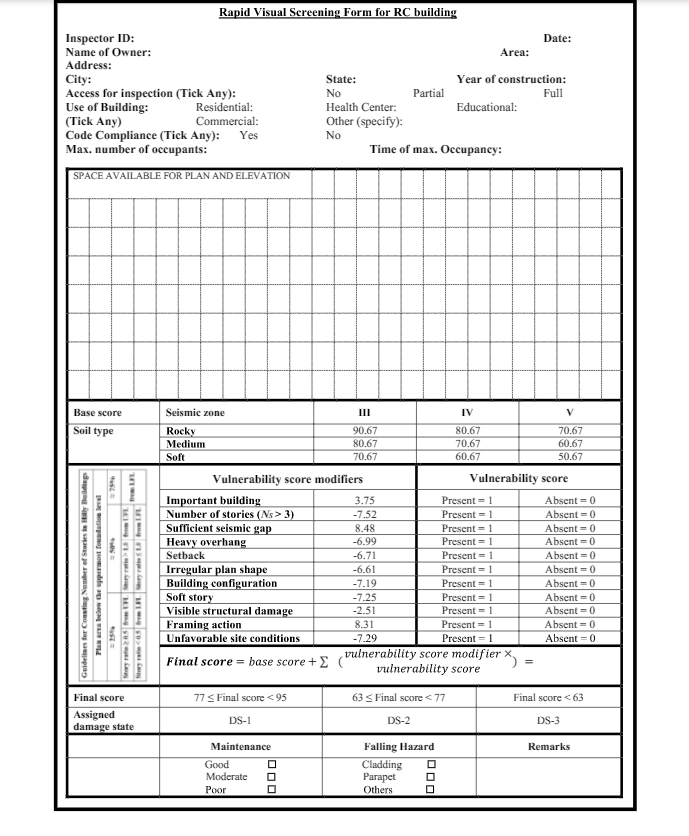
How is that this evaluation performed?
Yati illustrates with an instance. “Suppose a constructing is located in Shimla (Seismic zone IV) on rocky strata and it has residential occupancy. Furthermore, it has a comfortable story, irregular plan form, no hole between two buildings, and basis at a number of ranges. The plan space beneath the uppermost basis degree (UFL) is sort of 75%. Variety of tales beneath and above the UFL is 2 and three, respectively,” she posits.
“Now, mark one akin to the options current within the constructing (variety of tales larger than three, irregular plan form, constructing configuration, comfortable story, framing motion) and nil akin to the options absent (vital constructing, enough hole between buildings, heavy overhang, setback, seen structural damages, unfavourable web site situations) within the constructing below remark within the proposed RVS type,” notes Yati.
“Utilizing the proposed modifiers for the irregular options current within the constructing, the obtained rating is 60.41, which is lower than 63 (out of 100). Thus, the thought-about constructing is predicted to have vital structural harm in case of a powerful earthquake,” she provides.
rating denotes that the constructing is predicted to have both no harm or minor non-structural harm. An anticipated vulnerability rating (EVS) larger than or equal to 77 displays an excellent rating for a constructing. EVS lower than 77 and larger than or equal to 63 reveals that the constructing is predicted to have main non-structural damages and reasonable structural damages. EVS lower than 63 reveals vital structural harm.
Via intensive discipline surveys, researchers have collected a considerable amount of knowledge on the kinds of buildings current within the Mandi area of the Himalayas and the everyday attributes current in these buildings which are related to their earthquake vulnerability.
A numerical research was additionally carried out to ascertain pointers for counting the variety of tales in hilly buildings for his or her RVS. Additional, based mostly on the weak traits current in buildings, an improved RVS methodology was proposed.
“The vulnerability options utilized in our proposed methodology for speedy visible screening of bolstered concrete buildings accounts for almost all of the development practices adopted within the Indian Himalayan area. Though the intensive survey was carried out in Mandi, the constructing typologies, native bylaws and the kind of damages confronted by RC buildings, in another cities within the Himalayas through the previous earthquakes, have been completely studied,” claims Dr Saha.
“It was famous that the buildings manufactured from RC have widespread options. Subsequently, the proposed RVS methodology is predicted to be helpful within the bigger Himalayan area,” he provides.
The methodology developed for screening buildings is an easy single-page RVS type that doesn’t require a lot experience to fill. It takes into consideration the varied vulnerability attributes which are distinctive to the buildings within the case research area.
Calculations made utilizing these observations produce a seismic vulnerability rating for buildings, which differentiates weak buildings from the extra strong ones, and permits higher decision-making for upkeep and restore. The computation course of is designed such that it minimises the potential of human bias or subjectivity of the assessor in scoring a constructing.
“The proposed methodology ensures minimal human bias because the assessor has to mark just one or zero in opposition to the presence or absence, respectively, of thought-about vulnerability options. It doesn’t rely on the person assessor’s notion/understanding concerning the impact of a typical function on the constructing’s efficiency,” explains Yati.
“RVS research are sometimes carried out by low-skilled individuals, with minimal or no formal coaching. Subsequently, except an accessor has enough background data concerning the behaviour of a constructing and its numerous parts below earthquake shaking, that individual could miscalculate the vulnerability. Within the proposed methodology, we tried to minimise that requirement. We now have introduced an expression after intensive analyses combining our personal expertise from the sphere surveys and several other established data, about seismic behaviour of buildings and its parts, introduced in nationwide and worldwide design pointers,” says Dr Saha.

Learning the issue
The authors have been analysing the weak scenario of the constructed surroundings within the Indian Himalayan area for the final 5 years or so.
“A serious problem we at all times face is the unavailability of dependable knowledge, be it concerning the present buildings or concerning the damages occurred throughout previous earthquakes. Additionally, in India the place robust earthquakes aren’t very frequent, convincing widespread folks to put money into making certain seismic security is tough,” says Dr Saha.
Whereas speaking about the advantages of the analysis, Aggarwal notes, “We now have proven that the proposed methodology is beneficial for segregating bolstered concrete buildings in hilly areas in keeping with the harm that they’re anticipated to expertise within the occasion of an earthquake.”
What recommendation would the authors provide residents dwelling within the Himalayan area?
“We don’t recommend refraining from developing RC constructions within the Himalayan area. Our intention is to inspire the residents to strictly comply with earthquake resistant design pointers whereas developing their homes and ask for high quality building. For any alteration to present buildings one should completely assess the implications of such alteration on the earthquake security. We now have an abundance of pointers for earthquake resistant design and building practices. What is required is to implement them rigorously on the grassroot degree,” says Dr Saha.
“We should realise that earthquake-proof buildings aren’t virtually doable to assemble because the earthquake itself is unknown. Our goal ought to be to minimise the danger of earthquake induced damages by following earthquake resistant design-construction practices,” he provides.
Each Dr Saha and Yati argue that if the constructing is properly designed as per the rules of earthquake resistant design, there isn’t a restrict on the variety of tales an individual can assemble.
“Nonetheless, it is rather vital to comply with the constructing bylaws together with design pointers whereas developing any constructing in a area,” says Dr Saha. In the meantime, residents concerned within the building of their very own houses or constructions within the Himalayas can look out for sure options.
“Presence of structural irregularities, akin to comfortable story, floating columns, irregular plan form, use of brick columns intermittently as a substitute of bolstered concrete columns, inadequate distance between buildings, heavy overhangs, and many others, make buildings weak to seismic hazard. If the resident is concerned within the design and building part of the constructing then they need to guarantee correct ductile detailing of the structural members (beam, column, slab, and many others.). Furthermore, particular consideration is required whereas designing and developing buildings resting on slopes,” he says.
The evaluation of buildings within the Himalayan area is pressing and important not solely due to the area’s basic earthquake vulnerability but in addition as a result of an enormous earthquake is predicted anytime because of the “seismic hole” of the previous two centuries. It’s believed {that a} seismic hole (the absence of a big earthquake) represents the time taken to build up stress, which is then launched in a big earthquake. It’s time that human habitats in these areas are bolstered in order that they will stand up to any delicate or extreme earthquakes which will happen sooner or later.
(Edited by Divya Sethu)
(Characteristic picture of Dr Sandip Kumar Saha and Ms Yati Aggarwal courtesy IIT-Mandi. Different photographs courtesy Right down to Earth, Wikimedia Commons.)
Further Sources:
Aggarwal, Y., and Saha S. Ok. (2022). An Improved Speedy Visible Screening Technique for Seismic Vulnerability Evaluation of Strengthened Concrete Buildings in Indian Himalayan Area, Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 1-29.