The evolution of various kinds of herbivorous Triassic dinosaurs was helped by local weather change and this performed a key function of their rise to dominance of terrestrial ecosystems throughout the Mesozoic. Writing within the tutorial journal “Present Biology”, the researchers, which embody Professor Richard Butler (College of Birmingham), postulate that it was local weather change fairly than competitors that performed a key function within the ascendancy of the Dinosauria.

Image credit score: Victor O. Leshyk
Triassic Dinosaurs
The scientists conclude that international local weather change related to the Triassic-Jurassic mass extinction occasion, which occurred roughly 201 million years in the past, worn out many kinds of terrestrial vertebrate and this opened up ecosystems for the Dinosauria to take advantage of. Massive herbivores such because the Aetosauria (eagle lizards) died out and this permitted the Sauropodomorpha to diversify.

Sauropods Profit
The lizard-hipped sauropods (Sauropodomorpha), particularly, have been capable of thrive and transfer into new territories because the Earth grew hotter after the end-Triassic mass extinction occasion.
Different scientists concerned embody researchers from Bristol College, the College of São Paulo (Brazil) and the Friedrich-Alexander College Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), in Germany.
Pc Generated Fashions of International Local weather Change
Pc generated fashions of palaeoclimates and adjustments to rainfall and temperature gradients have been created utilizing the intensive Paleobiology Database because the supply of reference supplies. The research demonstrated that the long-necked sauropods turned extra specious and geographically numerous because the planet skilled a interval of worldwide warming.
Dr Emma Dunne, a lecturer in palaeontology at FAU and one of many authors of the paper printed in the present day said:
“What we see within the information means that as an alternative of dinosaurs being outcompeted by different giant vertebrates, it was variations in local weather circumstances that have been proscribing their range. However as soon as these circumstances modified throughout the Triassic-Jurassic boundary, they have been capable of flourish.”
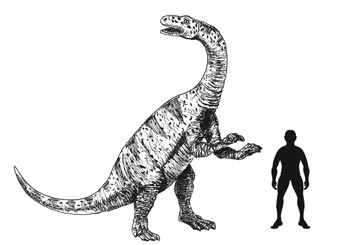
Image credit score: All the pieces Dinosaur
The image (above) exhibits a scale drawing of Lufengosaurus (L. huenei), from the Early Jurassic of south-western China. Based on the researchers, sauropodomorphs like Lufengosaurus benefitted from a warming world allowing all these herbivorous dinosaur to thrive.
Dr Dunne added:
“The outcomes have been considerably stunning, as a result of it seems that sauropods have been actually fussy from the get-go: later of their evolution they proceed to remain in hotter areas and keep away from polar areas.”
All the pieces Dinosaur shares the CollectA Age of Dinosaurs Well-liked vary that incorporates a number of replicas of Triassic and Jurassic sauropodomorphs: CollectA Age of Dinosaurs Well-liked Vary.
Professor Richard Butler commented:
“Local weather change seems to have been actually vital in driving the evolution of early dinosaurs. What we wish to do subsequent is use the identical methods to grasp the function of local weather within the subsequent 120 million years of the dinosaur story”.
All the pieces Dinosaur acknowledges the help of a media launch from the College of Birmingham within the compilation of this text.
The scientific paper: “Climatic controls on the ecological ascendancy of dinosaurs” by Dunne et al printed in Present Biology.